MongoDB Data Adapter
The MongoDB data adapter in Graylog enables the ingestion of data from a MongoDB database into Graylog for analysis, monitoring, and visualization. It stores keys and values in the Graylog configuration database, allowing entries to be modified using pipeline functions or REST API calls. This flexibility lets you dynamically adjust lookup table results based on incoming log data or external sources, enhancing the adaptability of your log management workflows.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
-
A valid Graylog Enterprise license is required.
Configure the Data Adapter
You can create a data adapter during the lookup table creation workflow, or they can be created separately on the Data Adapters tab. The following configuration options are available for this data adapter:
|
Title |
A short and unique title for this data adapter. |
|
Description |
Data adapter description. |
|
Name |
The name used to refer to this data adapter. This should be something unique and recognizable within your Graylog environment. |
|
Custom Error TTL |
Time-to-live for custom error messages in seconds. This controls how long custom error responses are cached. If no value is specified, the default is 5 seconds. |
|
CIDR lookup |
Enable this checkbox if the keys in the lookup table are in CIDR notation and lookups are done with IP addresses. See CIDR Lookup below for more information about this option. |
CIDR Lookup in MongoDB Data Adapters
A Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) address is an IP address ending in a slash. The number following the slash represents the number of addresses in the range.
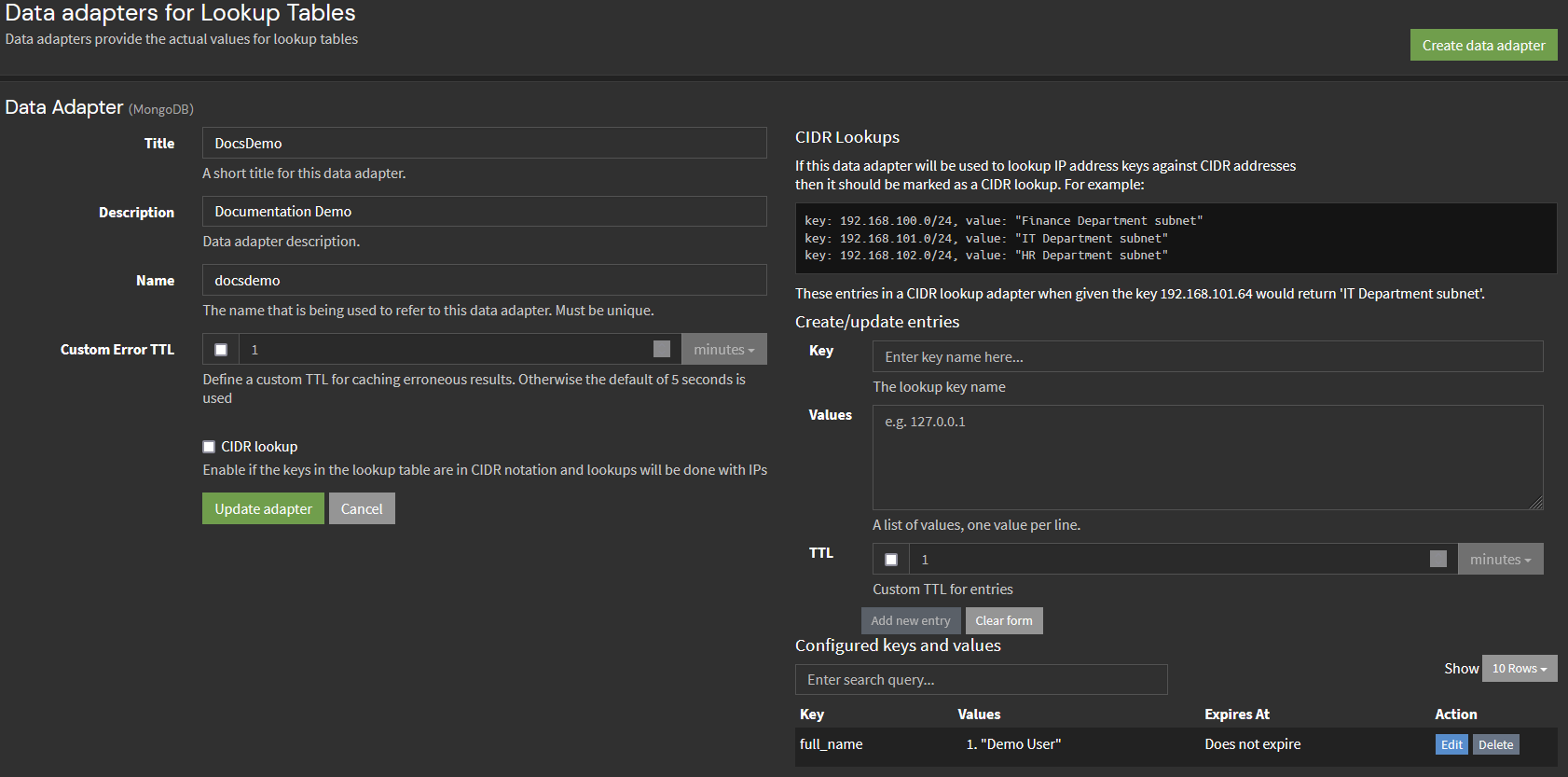
The CIDR lookup option is a checkbox at the bottom of the data adapters configuration page. If you do not select this option, the data adapter performs exact key matching and looks for an identical pattern. If you select the CIDR lookup option, lookups compare the key (which must be an IP address) to the CIDR address keys of the adapter. The CIDR addresses are searched to find a matching IP address.
An example list of key value pairs:
key: 192.168.100.0/24, value: "Finance Department subnet"
key: 192.168.101.0/24, value: "IT Department subnet"
key: 192.168.102.0/24, value: "HR Department subnet"
In this case, a lookup on the IP address 192.168.101.117 would return “IT Department subnet.”
Update the Data Adapter via the REST API
To learn how to interact with the MongoDB data adapter via the REST API, access the API browser at api/api-browser/#!/Plugins/MongoDBDataAdapter. This interface allows you to add, update, list, and delete key-value pairs for the data adapter. The data_adapter_id required for these operations can be retrieved from the System > Lookup API endpoint.
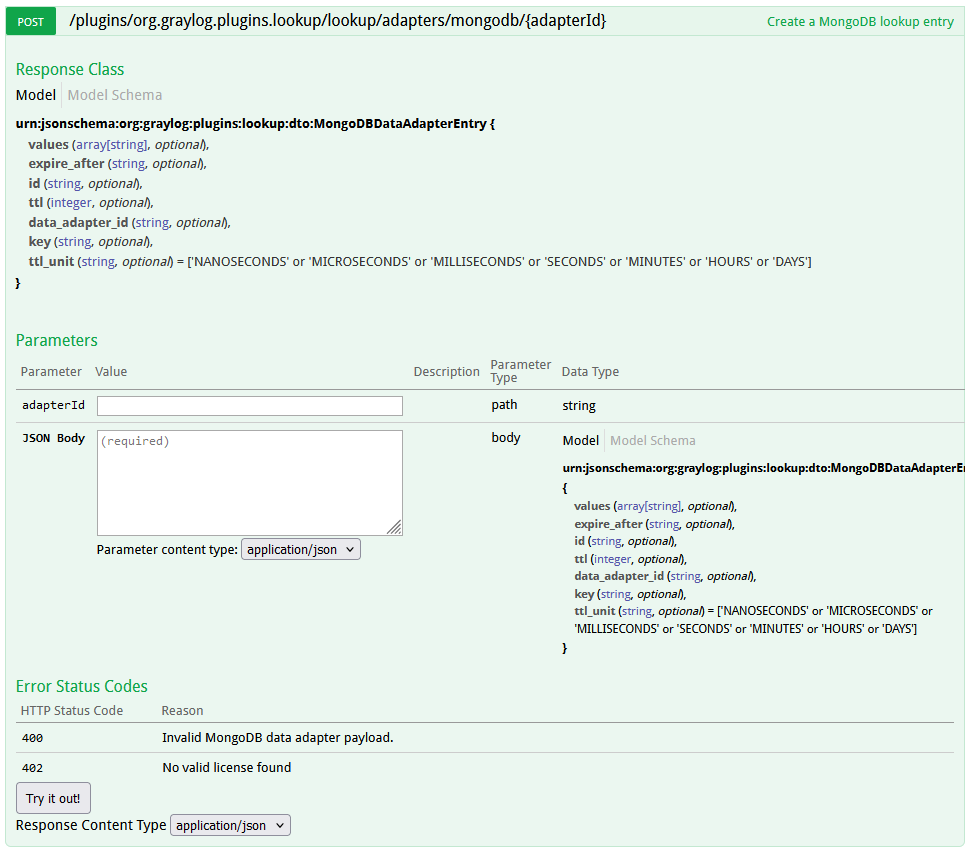
Here is an example of how to add a key to a MongoDB adapter with an API token:
curl -u d2tirtpunshmgdsbq5k3j0g4ku230ggruhsqpa0iu7mj1lia55i:token \
-H 'X-Requested-By: cli' -H 'Accept: application/json' \
-X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:9000/api/plugins/org.graylog.plugins.lookup/lookup/adapters/mongodb/mongodb-data-name' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary $'{\n"key": "myIP",\n"values:["12.34.42.99"],\n"data_adapter_id":"5e578606cdda4779dd9f2611"\n}'Update from the GUI
The values of the MongoDB adapter can also be altered directly via the user interface. Select your data adapter then click the Edit action button to create/update entries.
Add Context with Pipelines
Using the lookup() function in Graylog's pipeline rules allows you to retrieve data from a lookup table and use it to create or update fields in your log messages. This feature is a powerful way to enrich your logs with additional context or metadata.
The lookup() function retrieves data from a specified lookup table using a key. The syntax is:
lookup("lookup_table_name", key);
lookup_table_name: The name of the lookup table you've configured in Graylog.key: The value used to search in the lookup table. This is often a field from your log message.
The function returns:
- A single value if the lookup table is configured to return a single value.
- A map (key-value pairs) if the lookup table returns multiple values.
Pipeline Example
Here is an example workflow on using the lookup() function.
-
Before performing a lookup, check if the message contains the field you'll use as the key:
Copywhen
has_field("username") -
Use the
lookup()function within thethenclause to retrieve data from the lookup table:Copyuser_info = lookup("user_info_lookup_table", to_string($message.username)); -
Verify the lookup was successful (i.e. it did not return
null):Copyif (!is_null(user_info)) {
// Proceed to use the lookup data
} else {
// Handle the case where the lookup didn't find a match
} -
Use
set_field()to add new fields or update existing ones with the data retrieved.For a single-value lookup:
Copyset_field("full_name", user_infoFor a multi-value lookup:
Copyset_field("full_name", user_info["full_name"]);
set_field("email", user_info["email"]);
set_field("department", user_info["department"]);
An example pipeline rule may look as follows. This pipeline rule enriches log messages containing a username by looking up user information from the user_info_lookup_table. If found, it adds the user’s full name, email, and department to the message. If not, it adds a User not found error field.
rule "Enrich User Info"
when
has_field("username")
then
let user_info = lookup("user_info_lookup_table", to_string($message.username));
if (!is_null(user_info)) {
// Update or create fields with lookup data
set_field("full_name", user_info["full_name"]);
set_field("email", user_info["email"]);
set_field("department", user_info["department"]);
} else {
// Optionally handle cases where the lookup fails
set_field("lookup_error", "User not found in lookup table");
}
endFurther Reading
Explore the following additional resources and recommended readings to expand your knowledge on related topics:

