Get in Log Data
Getting the right log data into Graylog is the first step to building a centralized, actionable log management and security platform. Graylog offers several flexible methods for collecting and forwarding log data from diverse sources across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments. Choosing the right method ensures you can scale your log ingestion, maintain data quality, and optimize your environment for real-time analysis.
This article explains the log ingestion methods available in Graylog and provides general guidance on when to use each method.
Graylog Ingestion Architecture
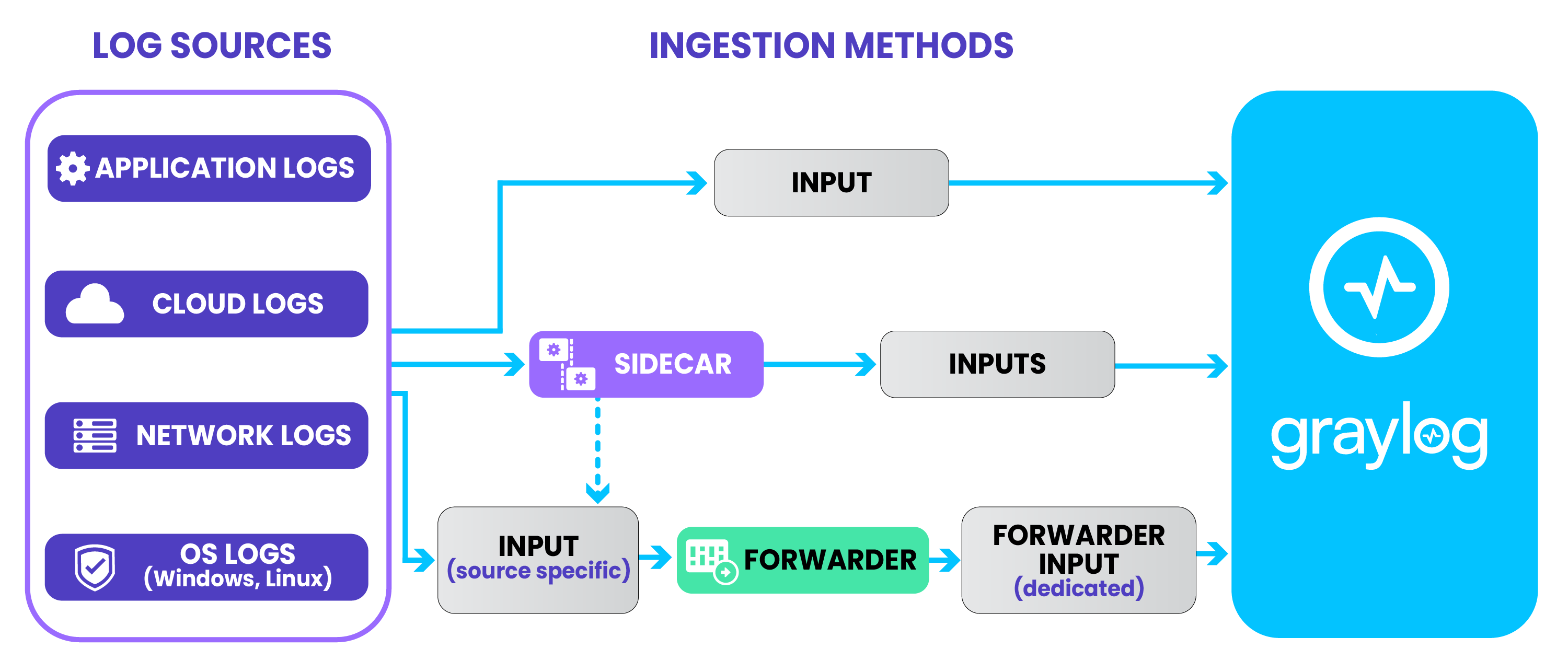
Graylog includes multiple architectural elements for log ingestion:
Inputs
A Graylog input is the primary entry point for receiving log messages from external sources.Each input is configured for a specific protocol or format. For example, you might configure a Syslog TCP input on port 5140 in Graylog to receive logs from network firewalls.
Common input types include:
-
Syslog UDP/TCP: Receives logs from routers, switches, and other network devices that send syslog messages.
-
GELF UDP/TCP/HTTP: Ingests Graylog Extended Log Format (GELF) messages from applications or containers.
-
Beats Input: Accepts logs from Filebeat or Winlogbeat.
-
JSON, Kafka, AMQP, and others: Supports advanced or scalable integrations.
Inputs can be configured on individual nodes or globally across the cluster. You can customize ingestion parameters such as port numbers, authentication settings, and message parsing options.
Inputs are ideal when applications or devices can send logs directly to Graylog.
For more information, including configuration information for each available input, see Inputs.
Inputs and Graylog Illuminate
Graylog Illuminate enhances log analysis by providing prebuilt packs that include parsing rules, dashboards, alerts, and more all tailored for common log sources. Illuminate helps users accelerate log processing and gain actionable insights without extensive manual configuration.
For complete information about Illuminate, including the available content packs, see the Illuminate documentation.
Sidecar
Graylog Sidecar is an optional component that manages log collector agents (e.g. Filebeat, Winlogbeat, NXLog). It acts as a centralized controller for deploying, configuring, and monitoring log collectors across multiple servers or endpoints without needing to manage each collector individually.
Sidecar is particularly effective in environments with a large or diverse set of log sources. It simplifies configuration management and ensures consistent logging practices at scale.
For complete information, including installation instructions, see Sidecar.
Forwarder
The Graylog Forwarder is a standalone agent used to transmit log data to Graylog Cloud or an on-premises Graylog server cluster. The Forwarder is designed to securely collect logs from distributed or remote environments and forward them back to your central Graylog cluster.
The Forwarder provides encrypted log transport to protect data in transit, uses buffering and queuing mechanisms to ensure reliable delivery even under adverse network conditions, and performs no local processing. Log data is simply passed through from the source to Graylog.
For complete information, including installation instructions, see Forwarder.
Plan for Log Ingestion
The most effective log ingestion approach depends on your environment, infrastructure, and the types of log sources you plan to bring into Graylog. Start by reviewing the following resources to determine the best path for your deployment:
-
Select and Ingest High-Value Log Sources: Learn how to evaluate and prioritize log sources based on the value they provide to your organization. This guide helps you focus on the data that best supports your security, compliance, and operational goals.
-
Log Source Ingestion Reference: Once you know which log sources you plan to collect, use this reference to find the supported integrations, input types, and configuration requirements for each.

