Apache HTTP Server on a Linux system. This pack will parse out and configure Apache2 access logs. It supports two access log formats: Common and Combined logs. And it supports "normal" logs and virtual hosts logs.
Supported Version(s)
-
Version 2.4.
Tested rsyslog Version
-
8.2212.0
What is Provided?
-
Parsing rules to extract Apache logs into Graylog schema-compatible fields. Apache logs get the GIM code “180200” (http.communication).
Stream Configuration
This technology pack includes one stream:
-
"Illuminate:Apache2 Device Messages"
Index Set Configuration
This technology pack includes one index set definition:
-
“Illuminate: Apache2 Messages”
Log Format Example
Access Logs
[30/Jan/2023:15:06:52 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 3477 "-" “Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/109.0::1 - Stefan [07/Feb/2023:16:38:37 +0000] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 487 "http://localhost/" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/109.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
Error Logs (beta, we support the following formats)
[Sun Jul 01 01:06:13 2022] [error] [client 1.2.3.4] File does not exist: /var/www/html/robots.txt[Wed Feb 01 00:00:01.584207 2023] [mpm_event:notice] [pid 745:tid 539654844431424] AH00999: Apache/9.4.41 (Ubuntu) configured -- resuming[Wed Jul 15 01:34:12.093005 2020] [proxy:error] [pid 139:tid 133316032] (13)Permission denied: AH00957: HTTP: attempt to connect to 127.0.0.1:9000 (127.0.0.1) failed
Supported SSL Log format (beta support)
[13/Aug/2022:05:41:26 +0600] 192.168.0.100 TLSv1.2 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 "GET /graylog/helper.php?cmd=gethelper HTTP/1.1" 1375
These SSL logs are custom logs; please configure your system accordingly. The custom file name is: httpd-ssl.log. These are default fields/values. Logs with non-default fields or order will not work.
Requirements
-
There are two ways to deliver logs that are supported: Filebeat (with Sidecar) and rsyslog.
-
The pack supports a non-standard log folder as long as the name (
access.log) does not change.
Input via Filebeat together with Graylog Sidecar
Please use the official Graylog Sidecar documentation to configure your Graylog server and your client(s).
-
Create an input and an API key and set up Graylog Sidecar.
-
Add your client(s), e.g. web server.
Graylog Server Settings
1. Create a global Beats input in Graylog.
2. Create a Graylog REST API access token and save it.
3. Create a (Linux) filebeat configuration under Sidercar > Configuration with a "filebeat on linux" collector.
4. Configure the file and add:
-
The correct IP (Graylog server IP) under hosts.
-
The log source configured to the desired value and a field
event_source_productwith the valueapache_httpd.
filebeat.inputs:
- input_type: log
paths:
- /var/log/apache2/access.log
- /var/log/apache2/error.log
- /var/log/apache2/httpd-ssl.log
type: filestream
fields_under_root: true
fields:
event_source_product: apache_httpd
event_source_product and - /var... .
This will only log Apache access logs, but you can add error logs, etc.
5. Finally, save the configuration.
Configure a Client with Filebeat and Graylog Sidecar
1. Install Sidecar on the remote machine.
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-sidecar-repository_1-5_all.deb
sudo dpkg -i graylog-sidecar-repository_1-5_all.deb
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install graylog-sidecar2. Edit the /etc/graylog/sidecar/sidecar.yml file and configure:
-
server_url: GraylogServerIP -
server_api_token: Your API token
sudo gedit /etc/graylog/sidecar/sidecar.yml
server_url: "http://192.168.122.52:9000/api/"
server_api_token: "65ol7edseo24mub8o7pu86h2rsr8j9fjjpimtrm9nrpbjso7cnv"
3. Install, enable, and verify the Sidecar service.
sudo graylog-sidecar -service install
sudo systemctl enable graylog-sidecar
sudo systemctl start graylog-sidecar
sudo systemctl status graylog-sidecar
4. Install filebeats according to the documentation. Or, here is the download link for the OSS version.
-
If you install it manually, install it again under
/etc/filebeat. -
If you install it via apt-get, then it is in the correct folder.
Example commands for Ubuntu:
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/oss-8.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-8.x.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install filebeat
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
sudo systemctl status filebeat5. Optional. Edit the filebeat.yml file as needed. You do this via the Sidecar configuration in Graylog.
6. Start the deamon.
7. If there is a permission issue, you can resolve with:
sudo chown root filebeat.yml8. In Graylog, assign a configuration to your machine.
Requirements for Input via rsyslog
-
A configured UDP (or
TCP_sysloginput on Graylog server). -
Installation of rsyslog via the official documentation.
-
A configured
rsyslog.conf.
For example /etc/rsyslog.conf with a UDP input at 1514 on IP 192.168.122.52:
# provides UDP syslog reception
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerRun 1514
*.* @192.168.122.52:1514;RSYSLOG_SyslogProtocol23Format-
A configured
02-apache2.conf.
You might need to create the configuration file with:
sudo gedit /etc/rsyslog.d/02-apache2.confIf it is in the correct folder, rsyslog will load the file automatically after restarting the rsyslog service.
Example for 02-apache2.conf to log access, ssl, and error logs:
module(load="imfile" PollingInterval="10" statefile.directory="/var/spool/rsyslog")
input(type="imfile"
File="/var/log/apache2/access.log"
Tag="apache2_http_access"
Severity="info"
Facility="local6")
input(type="imfile"
File="/var/log/apache2/error.log"
Tag="apache2_http_error"
Severity="info"
Facility="local6")
input(type="imfile"
File="/var/log/apache2/httpd-ssl.log"
Tag="apache2_http_ssl"
Severity="info"
Facility="local6")
local6.access @192.168.122.40:1514
Use this command to restart the service on Ubuntu:
sudo systemctl restart rsyslogYou can check the status with:
sudo systemctl status rsyslogNote that red lines may indicate problems.
Limitations
-
Error logs are beta; most formats compatible.
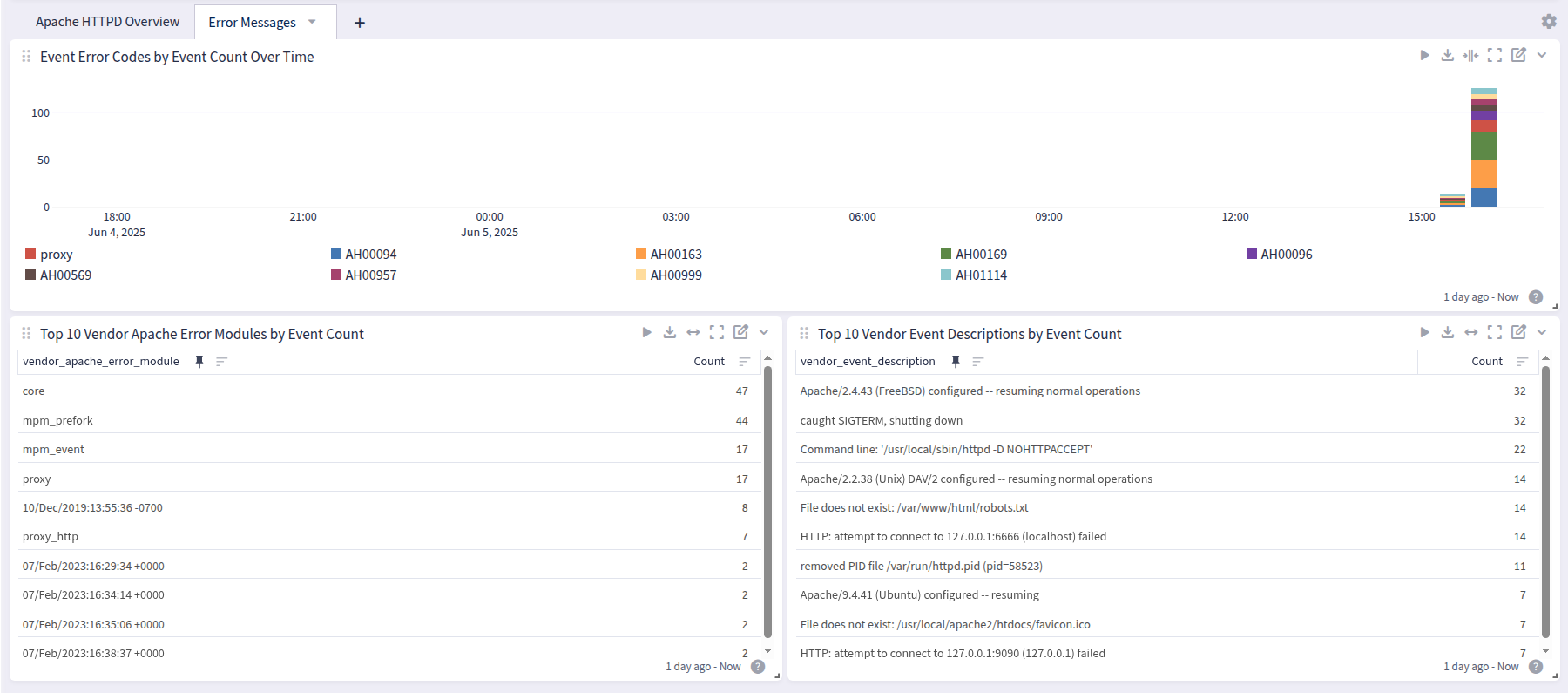
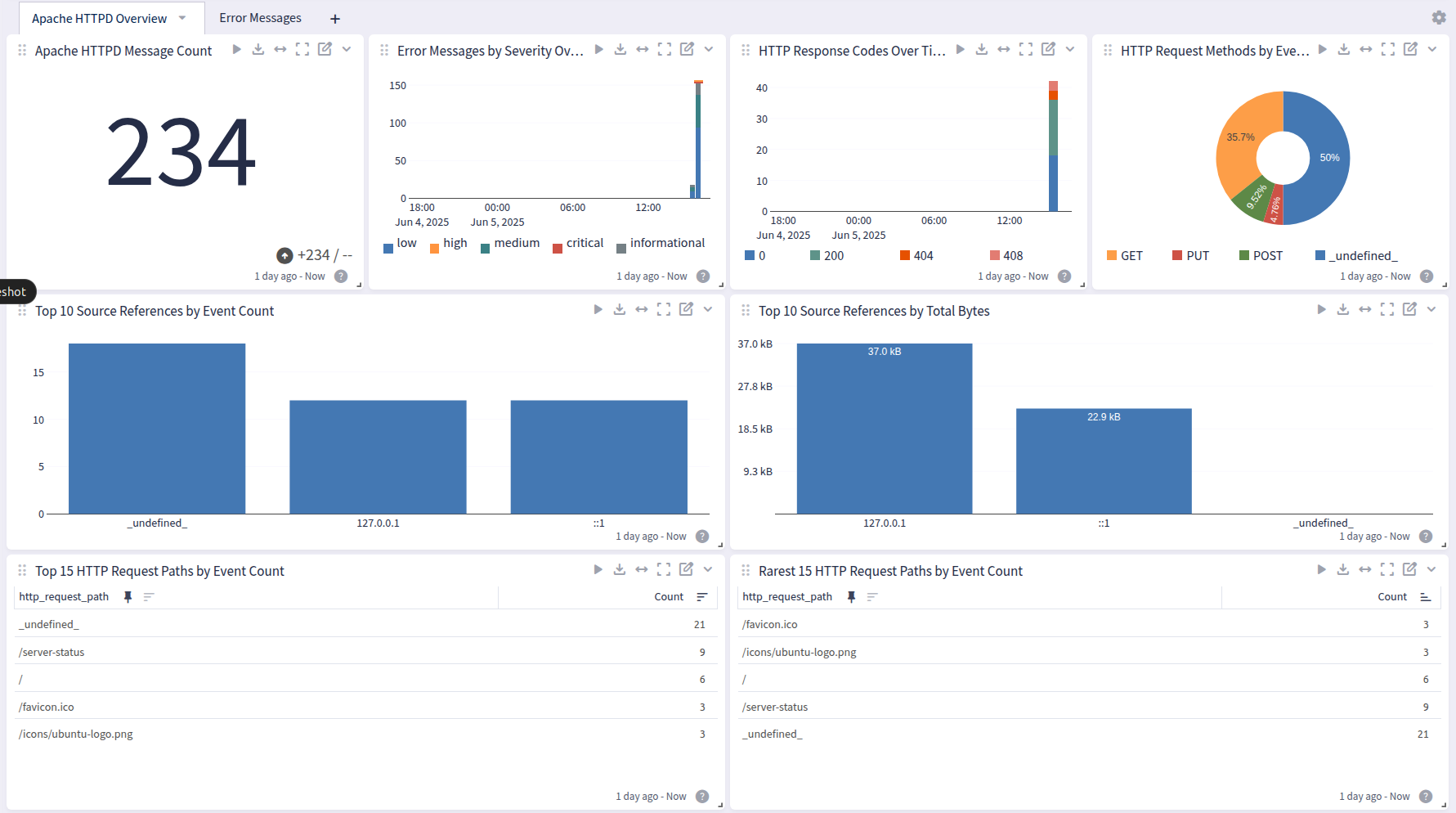
Dashboard
Apache HTTPD offers a dashboard with 2 tabs: Overview, New Incident, and HyperDetect Activity:
Overview
Error