Restore an Archive
After you set up Graylog archiving and have archived your first set of data, you can restore your archives when required, such as when you need to search and analyze the data.
Restore Archived Data
You may restore archived indices via the:
Note that Graylog restores all indices in the Restored Archives index set to avoid conflicts with the original indices (if they still exist).
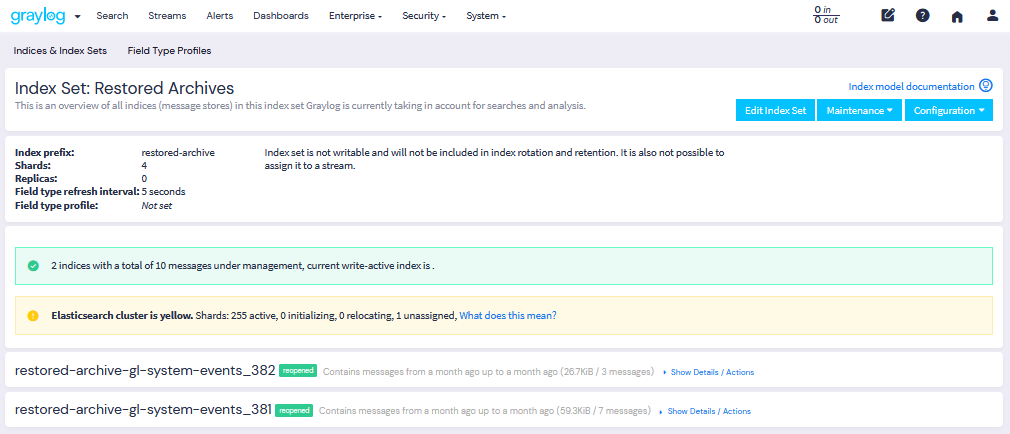
Restored indices are also marked as reopened, so they are ignored by index-retention jobs and are not closed or deleted. Therefore, you must manually delete restored indices when you no longer need them.
Restore Indices via the Graylog Interface
To restore an archive in the interface:
Navigate to Enterprise > Archives.
Select an index set from the Archive Catalog section.
Click the Restore Index button.
You may also restore or delete multiple index sets via the Bulk Actions drop down found next to the search box.
Restore Indices via the REST API
As with archive creation, you can also use the REST API to restore an archived index into the OpenSearch cluster:
$ curl -s -u admin -H 'X-Requested-By: cli' -X POST http://127.0.0.1:9000/api/plugins/org.graylog.plugins.archive/archives/graylog_386/restore
Enter host password for user 'admin': ***************
{
"archive_metadata": {
"archive_id": "graylog_307",
"index_name": "graylog_307",
"document_count": 491906,
"created_at": "2016-04-14T14:31:50.787Z",
"creation_duration": 142663,
"timestamp_min": "2016-04-14T14:00:01.008Z",
"timestamp_max": "2016-04-14T14:29:27.639Z",
"id_mappings": {
"streams": {
"56fbafe0fb121a5309cef297": "nginx requests"
},
"inputs": {
"56fbafe0fb121a5309cef290": "nginx error_log",
"56fbafe0fb121a5309cef28d": "nginx access_log"
},
"nodes": {
"c5df7bff-cafd-4546-ac0a-5ccd2ba4c847": "graylog.example.org"
}
},
"histogram_bucket_size": 86400000,
"source_histogram": {
"2016-04-14T00:00:00.000Z": {
"example.org": 227567
}
},
"segments": [
{
"path": "archive-segment-0.gz",
"size": 21653755,
"raw_size": 2359745839,
"compression_type": "SNAPPY"
"checksum": "751e6e76",
"checksum_type": "CRC32"
}
],
"index_size": 12509063,
"index_shard_count": 4
},
"system_job": {
"id": "e680dcc0-07a2-11e6-9e1b-fa163e6e9b8a",
"description": "Restores an index from the archive",
"name": "org.graylog.plugins.archive.job.ArchiveRestoreSystemJob",
"info": "Restoring documents from archived index: graylog_307",
"node_id": "c5df7bff-cafd-4546-ac0a-5ccd2ba4c847",
"started_at": "2016-04-21T09:24:51.468Z",
"percent_complete": 0,
"provides_progress": true,
"is_cancelable": true
}
}
The returned JSON payload contains the archive metadata and the system job description that runs the index-restore process.
Restore into a Separate Cluster
The added load from restored indices slows down your indexing speed. To avoid adding more load to your primary OpenSearch cluster, you can also restore the archived indices on a different cluster:
Transfer the archived indices to a different machine.
Place them in a configured backend.
Each index archive is in a separate directory, so if you only want to transfer one index to a different machine, copy the corresponding directory into the backend. For example:
$ tree /tmp/graylog-archive
/tmp/graylog-archive
├── graylog_171
│ ├── archive-metadata.json
│ └── archive-segment-0.gz
├── graylog_201
│ ├── archive-metadata.json
│ └── archive-segment-0.gz
├── graylog_268
│ ├── archive-metadata.json
│ └── archive-segment-0.gz
├── graylog_293
│ ├── archive-metadata.json
│ └── archive-segment-0.gz
├── graylog_307
│ ├── archive-metadata.json
│ └── archive-segment-0.gz
├── graylog_386
│ ├── archive-metadata.json
│ └── archive-segment-0.gz
└── graylog_81
├── archive-metadata.json
└── archive-segment-0.gz
7 directories, 14 files
Search in Restored Indices
Search queries automatically use restored indices. Every restored message in an index has a special gl2_archive_restored field with the value true, so you can search in restored messages using a query like:
_exists_:gl2_archive_restored AND <your search query>
If you want to exclude all restored messages from your query, use:
NOT _exists_:gl2_archive_restored AND <your search query>

