JSON Path from HTTP API Input
The JSON path value from HTTP API input reads any JSON response of a REST resource and stores a field value as a Graylog message.
Hint: This input can only target JSON primitive value nodes (numbers, text, strings, etc.) and not object and array nodes.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
-
You must have a remote server that produces a JSON document that the input can poll.
Input Type
This input is a
Input Configuration
Follow the input setup instructions. During setup of this input, you can configure the following options:
| Configuration Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Global |
Select this check box to enable the input on all Graylog nodes, or keep it unchecked to enable the input on a specific node. |
|
Node |
Select the node on which to start this input. If the Global check box is selected, this option is not available. |
|
Title |
Assign a unique title to the input. Example: |
|
URI of JSON resource |
Enter the URI for a resource that returns JSON on an HTTP request. |
|
Interval |
Set the time between every collector run. Example: If you set the Interval to |
|
Interval time unit |
Select a time unit from the drop-down menu. |
|
JSON path of data to extract |
Use standard JSON notation to enter the path to the value you want to extract from the JSON response. For example, you can utilize JSONPath to select the first
or only the first download count: You can learn more about JSONPath in the documentation. See the following example use case for more information. |
|
Message source |
Enter what to use as the source field of the resulting message. |
Allow throttling this input (Checkbox) |
Enables Graylog to stop reading new data for this input whenever the system falls behind on message processing and needs to catch up. |
HTTP method (optional) |
Select the HTTP method to use for the requests from the drop-down menu. The default value is GET. |
|
HTTP body (optional) |
Enter the HTTP body for requests. If you choose POST or PUT for HTTP method, this field is required instead of optional. |
|
HTTP content type (optional) |
Select the content type for requests. If you choose POST or PUT for HTTP method, this field is required instead of optional. |
|
Additional, sensitive HTTP headers (optional) |
Add a comma-separated list of HTTP headers containing sensitive information. For example, use this field to enter authorization credentials. Example: |
Additional HTTP headers (optional) |
Add a comma separated list of additional HTTP headers. Example: |
| No. of worker threads (optional) | This setting controls how many concurrent threads are used to process incoming data. Increasing the number of threads can enhance data processing speed, resulting in improved throughput. The ideal number of threads to configure depends on the available CPU cores on your Graylog server. A common starting point is to align the number of worker threads with the number of CPU cores. However, it is crucial to strike a balance with other server demands. |
|
Override source (optional) |
By default, the source is a hostname derived from the received packet. You can override the default value with a custom string. This option allows you to optimize the source for your specific needs. |
|
Encoding (optional) |
All messages need to support the encoding configured for the input. For example, UTF-8 encoded messages should not be sent to an input configured to support UTF-16. |
|
Flatten JSON |
Select this option to flatten the whole JSON. The result is returned as message fields. Example: |
JSON Path from HTTP API Use Case
To analyze GitHub release download data in Graylog, you can retrieve the download count of a release package using the following API call:
$ curl -XGET https://api.github.com/repos/YourAccount/YourRepo/releases/assets/12345
{
"url": "https://api.github.com/repos/YourAccount/YourRepo/releases/assets/12345",
"id": 12345,
"name": "somerelease.tgz",
"label": "somerelease.tgz",
"content_type": "application/octet-stream",
"state": "uploaded",
"size": 38179285,
"download_count": 9937,
"created_at": "2013-09-30T20:05:01Z",
"updated_at": "2013-09-30T20:05:46Z"
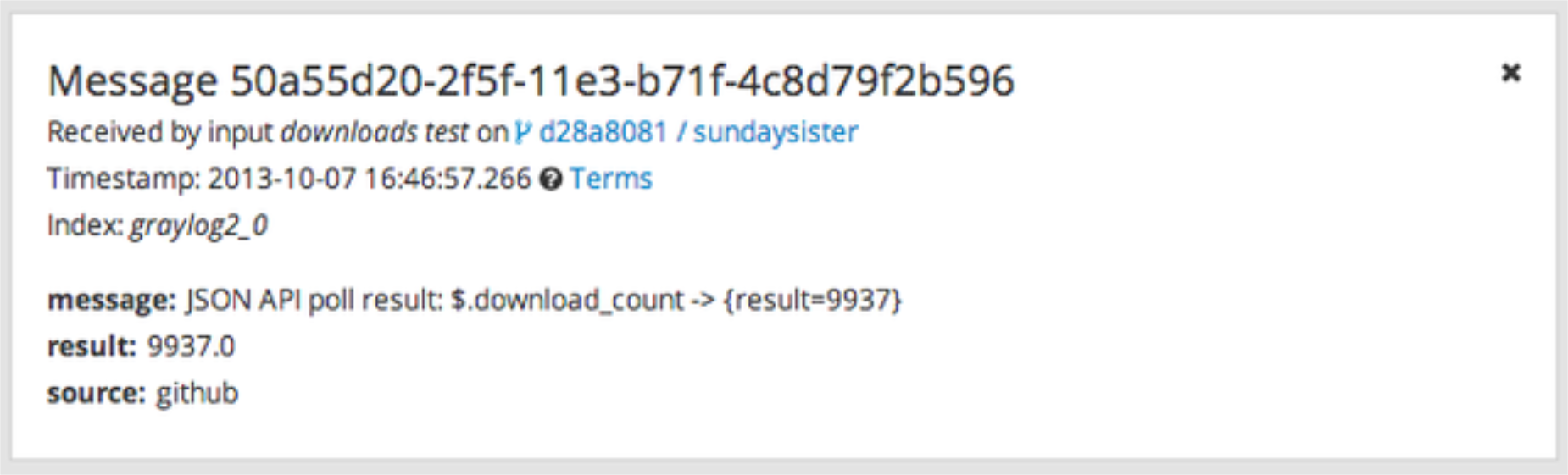
}The attribute we want to extract is download_count so we set the JSON path to $.download_count.
The result is a message in Graylog that looks like this:
Next Steps
After you complete input setup, visit Input Diagnosis for testing and validation of the new input. Use this functionality to help troubleshoot any connection issues.
Further Reading
Explore the following additional resources and recommended readings to expand your knowledge on related topics:

