The functionality Graylog REST API is very comprehensive; even the Graylog web interface is exclusively using Graylog REST API to interact with the Graylog cluster.
To connect to the Graylog REST API with a web browser, just add api/api-browser to your current http_publish_uri
For example if your Graylog REST API is listening on https://192.168.178.26:9000/api/, the API browser will be available at https://192.168.178.26:9000/api/api-browser/.
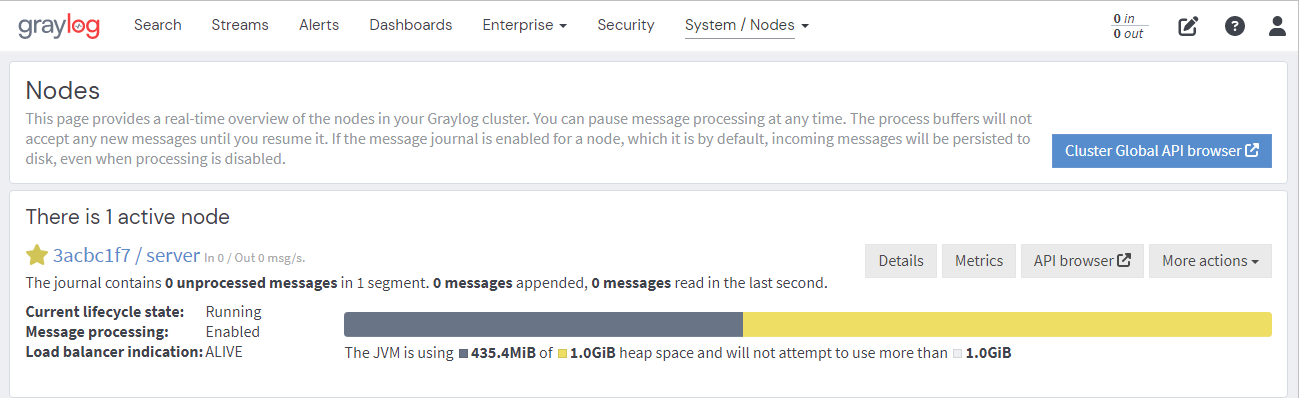
Using the API Browser
After providing the credentials (username and password), you can browse all available HTTP resources of the Graylog REST API.
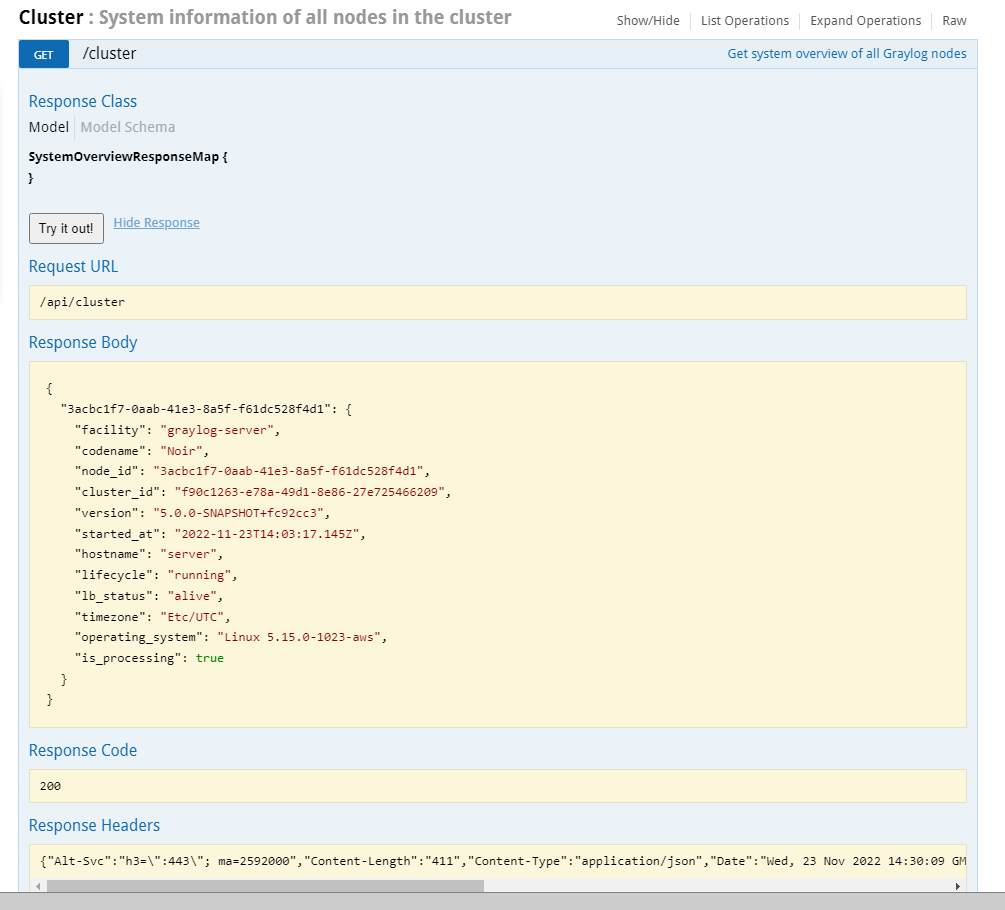
Interacting with the Graylog REST API
While having a graphical UI for the Graylog REST API is perfect for interactive usage and exploratory learning, the real power unfolds when using the Graylog REST API for automation or integrating Graylog into another system, such as monitoring or ticket systems.
Naturally, the same operations the API browser offers can be used on the command line or in scripts. A very common HTTP client being used for this kind of interaction is curl.
The following command displays Graylog cluster information as JSON, exactly the same information the web interface is displaying on the System / Nodes page:
curl -u GM:superpower -H 'Accept: application/json' -X GET 'http://192.168.178.26:9000/api/cluster?pretty=true'
The Graylog REST API will respond with the following information:
{
"71ab6aaa-cb39-46be-9dac-4ba99fed3d66" : {
"facility" : "graylog-server",
"codename" : "Smuttynose",
"node_id" : "71ab6aaa-cb39-46be-9dac-4ba99fed3d66",
"cluster_id" : "3adaf799-1551-4239-84e5-6ed939b56f62",
"version" : "2.1.1+01d50e5",
"started_at" : "2016-09-23T10:39:00.179Z",
"hostname" : "gm-01-c.fritz.box",
"lifecycle" : "running",
"lb_status" : "alive",
"timezone" : "Europe/Berlin",
"operating_system" : "Linux 3.10.0-327.28.3.el7.x86_64",
"is_processing" : true
},
"ed0ad32d-8776-4d25-be2f-a8956ecebdcf" : {
"facility" : "graylog-server",
"codename" : "Smuttynose",
"node_id" : "ed0ad32d-8776-4d25-be2f-a8956ecebdcf",
"cluster_id" : "3adaf799-1551-4239-84e5-6ed939b56f62",
"version" : "2.1.1+01d50e5",
"started_at" : "2016-09-23T10:40:07.325Z",
"hostname" : "gm-01-d.fritz.box",
"lifecycle" : "running",
"lb_status" : "alive",
"timezone" : "Europe/Berlin",
"operating_system" : "Linux 3.16.0-4-amd64",
"is_processing" : true
},
"58c57924-808a-4fa7-be09-63ca551628cd" : {
"facility" : "graylog-server",
"codename" : "Smuttynose",
"node_id" : "58c57924-808a-4fa7-be09-63ca551628cd",
"cluster_id" : "3adaf799-1551-4239-84e5-6ed939b56f62",
"version" : "2.1.1+01d50e5",
"started_at" : "2016-09-30T13:31:39.051Z",
"hostname" : "gm-01-u.fritz.box",
"lifecycle" : "running",
"lb_status" : "alive",
"timezone" : "Europe/Berlin",
"operating_system" : "Linux 4.4.0-36-generic",
"is_processing" : true
}
Creating and Using an Access Token
For security reasons, using the username and password directly on the command line or in some third party application is undesirable.
To prevent having to use the clear text credentials, Graylog allows to create access tokens which can be used for authentication instead.
The following example will create an access token named agents for the user graylog-sidecar:
- Navigate to the Users Overview menu
System / Users and Teams.
- Select the user you want to create a token for and click on
Edit tokens.

- Give the token a name and create it.
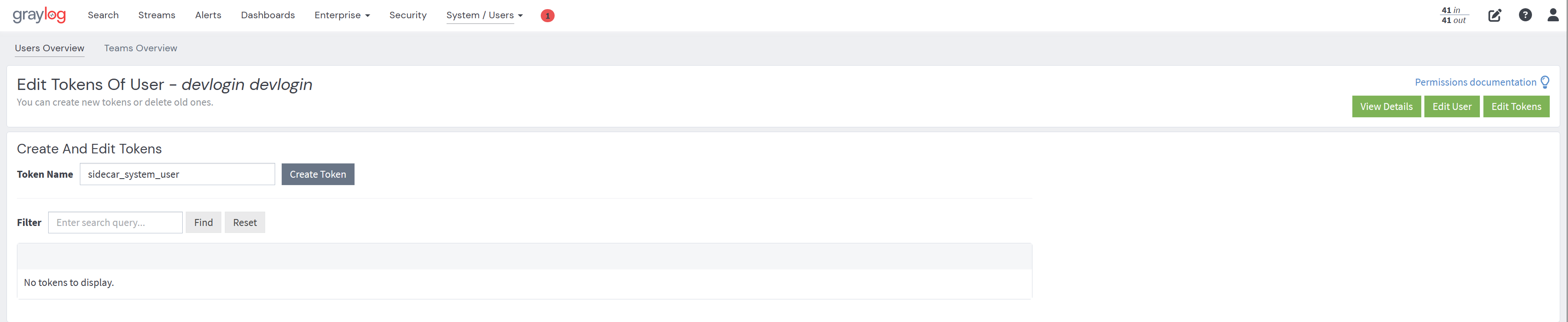
- You should now see the token in the list.
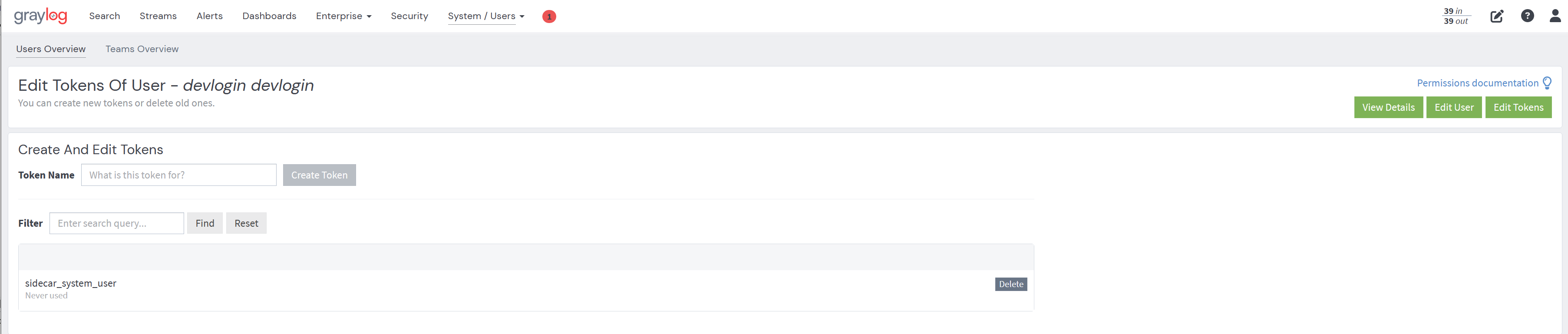
Either by unchecking the hide option or by copying the token to the clipboard you can access the token. The received access token can now be used as username in a request to the Graylog REST API using Basic Auth together with the literal password token.
When an access token is no longer needed, it can be delete on the Graylog UI via the Delete
Creating and Using Session Tokens
While access tokens can be used for permanent access, session tokens will expire after a certain time. The expiration time can be adjusted in the user’s profile.
Getting a new session token can be obtained via POST GM:
curl -i -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Accept: application/json' -H 'X-Requested-By: cli' 'http://192.168.178.26:9000/api/system/sessions' -d '{"username":"GM", "password":"superpower", "host":""}'
The response will include the session token in the field session_id
{
"valid_until" : "2016-10-24T16:08:57.854+0000",
"session_id" : "cf1df45c-53ea-446c-8ed7-e1df64861de7"
}
The received token can now be used as username in a request to the Graylog REST API using Basic Auth together with the literal password session.
Now a curl
curl -u cf1df45c-53ea-446c-8ed7-e1df64861de7:session -H 'Accept: application/json' -X GET 'http://192.168.178.26:9000/api/cluster?pretty=true'
